26 / 11 / 2024
What is the difference between tempered, toughened and laminated glass?
Within the glass industry, there are two main priorities; durability and safety. Although used widely across a range of industries, different types of glass have their own benefits for various uses. One variety of glass commonly used now is toughened glass, often referred to as safety glass. But what’s the difference between toughened glass, tempered glass, and laminated glass?
This blog will delve into the world of glass, its varieties and uses, and the benefits each serves to its purpose.

An Overview of Glass
Before exploring the varieties of glass, it can be helpful to understand the bare bones of what glass is and how it’s generally made.
Everyone knows that glass is a solid, transparent material that we see everywhere from building windows to car windscreens. But how is it made? Well, glass is a blend of natural raw materials, including sand, soda ash and limestone. These materials, together, are melted at an extremely high temperature until they come together to form molten glass. From here, we can form panes, vases, and lightbulbs, giving us abundant opportunities to utilise glass.
Glass manufacturing actually dates way back to 3500 BC. Since then we have discovered lots of different uses for it, more updated processes, and even different glass types. So, what are these different types of glass?
What is Toughened Glass?
Firstly, we’ll start out by exploring toughened glass. Toughened glass is a type of safety glass that undergoes special heat treatment to enhance its strength characteristics. The term toughened glass is actually often interchanged with tempered glass as they are technically the same thing. The term ‘tempered’ refers to the process that glass goes through in order to create safety/toughened glass.
So, toughened or tempered glass is a high, heat-strengthened safety glass that is up to 5 times stronger than ordinary, untreated glass. Here’s how it’s made:
Manufacturing Process
The process starts out with a standard pane of glass. This glass is heated up to around 650°C then it is rapidly cooled in a process called ‘quenching’. This process makes the outer layer of glass extremely durable due to compression so that it is excellent at withstanding impact or temperature changes. The inside of the glass is left under tension creating a balance of stress. The purpose of this is to not only create a strong and durable pane of glass but to also enhance its safety features where if the glass breaks, it shatters into small, rounded pieces that are much less likely to pierce the skin if it comes into contact with someone.
Key Properties
- Strength: One of the standout features of tempered/toughened glass is its strength, with it being up to 5 times stronger than regular glass.
- Safety: Another key feature is the safety applications toughened/tempered glass boasts, with its ability to shatter into small, rounded pieces, reducing the risk of injury.
- Temperature resistance: Due to the rapid changes in temperature during the manufacturing process, tempered/toughened glass is able to withstand large fluctuations in temperature, meaning it is used often in high or low-temperature environments.
Applications
Thanks to its strength and safety features, toughened glass is used across a variety of industries and applications. They include:
- Vehicles: Toughened glass is used in car windows, protecting driver and passenger safety in case of a crash.
- Furniture: Toughened glass is also used for things such as glass tables or other features around the home like shower doors.
- Technology: If you’ve ever bought a phone screen protector or replacement, you’ll often find they are made of tempered glass.
- Buildings: As mentioned above, toughened glass is resistant to temperature fluctuations, meaning it is used widely in buildings, especially those in hot or cold environments.
Limitations
Finally, it is important to note that there are some limitations with toughened glass, one being that once it has become toughened, you are unable to cut or drill it to size. When creating toughened glass panels, the size must be established before the tempering process as attempting to reshape afterwards would result in the glass breaking. This means that the planning stage of installing glass partitions in an office, for example, is extremely important as all the measurements must be taken perfectly beforehand. Find out more about the process of installing glass office partitions.
What is Laminated Glass?
The second type of glass we are exploring is called laminated glass. Laminated glass is also a type of safety glass, although it differs in structure and composition. Here’s how it’s made.
Manufacturing Process
Laminated glass is made from two different structures; glass and a plastic interlayer. This interlayer is usually made from either EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate) or PVB (polyvinyl butyral) and is sandwiched between two panes of glass. A pressure roller forms one pane of laminated glass from two regular glass panes and one layer of plastic. The heat and compression from the roller mechanically and chemically bond each layer together. Laminated glass is classed as a type of safety glass due to the way in which it shatters. Unlike tempered/toughened glass, laminated glass, when broken, holds the fragments of glass together due to the plastic interlayer.
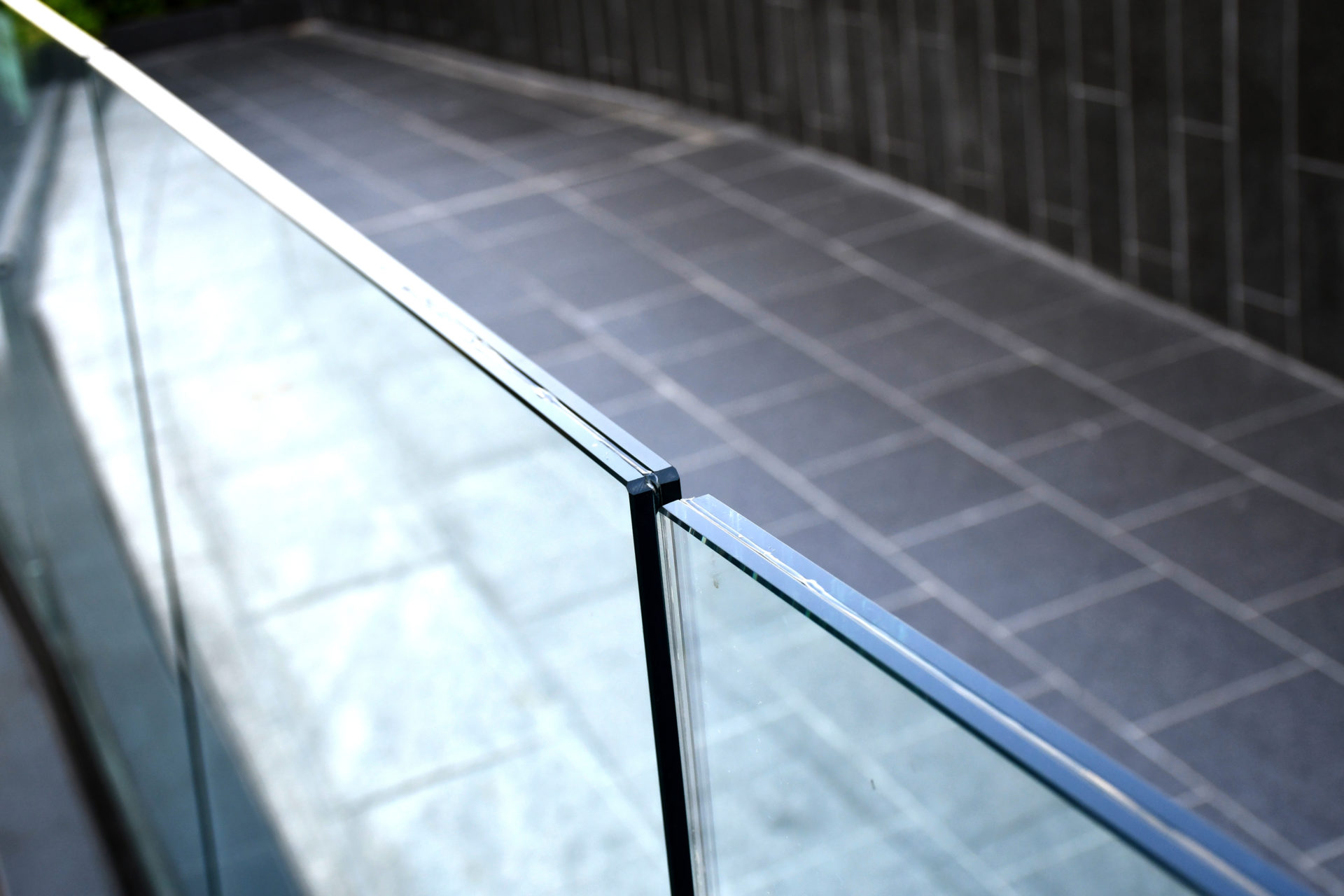

Key Properties
- Strength: As with toughened glass, laminated glass is much stronger than regular glass due to the extra layers and plastic interlayer, making it more resistant to penetration.
- Safety: As above, laminated glass is much safer to be around if broken as the plastic interlayer keeps the broken fragments together, reducing the risk of injury.
- Soundproof: Laminated glass is often a term used to describe acoustic glass due to its excellent soundproofing abilities. The plastic interlayer helps absorb more sound than single and even double-glazing glass would. Read more about Acoustic Glass.
- UV Protection: One final advantage of laminated glass you may not think about is its ability to block up to 99% of harmful UV rays. This is ideal for hot climates, protecting interiors from damage or sun fading.
Applications
Due to the differences in characteristics between toughened and laminated glass, the latter is more commonly used where natural elements may take greater effect, such as:
- Windshields: A car windshield is one of your most important protection features in case of an accident so laminated glass is preferred over toughened glass as it will not shatter into a thousand pieces (impact resistant) and will protect you from the sun when driving.
- Skylights: Again, laminated glass is excellent at absorbing the sun’s harmful UV rays, so is the ideal choice for skylights and other roof windows.
- Security: Due to its structure and ability to remain intact, even when broken, laminated glass is used in high-security environments, such as banks.
- Aquariums: Water is heavy, so strong glass walls are needed in places such as aquariums to withstand the pressure. Also, if an aquarium wall were to break, water is less likely to spill out everywhere, unlike toughened glass which would shatter on impact.
Limitations
One of the more notable limitations of laminated glass is the cost of production. Generally, laminated glass is heavier and more expensive to make than other forms of safety glass so budget can impact the decision to use it.
Toughened Glass or Laminated Glass?
Finally, now we’ve explored the differences between toughened/tempered glass and laminated glass, you might be wondering how to choose between them. It all comes down to what your priorities are, and where you are going to use it.
If safety is your primary concern, toughened glass may be your first choice, particularly if it’s for use in windows, doors and furniture, such as glass office partitions. The same can be said if strength is your priority as toughened glass is ideal in high-impact scenarios.
If security or noise reduction is your number one priority, you might want to consider laminated glass due to its unparalleled noise absorption qualities, UV protection and enhanced security.
Knowing the difference between toughened/tempered glass and laminated glass can be a huge time and money saver when planning a project. It can be useful to think about your priorities before selecting your glass, as each type’s unique qualities can make a world of difference in the long run.
If you would like to speak with a professional, contact us today and a member of our expert team will be happy to assist you.
Enjoy this article? You might be interested in some of our others:
20 / 12 / 2024
Express Building Manchester Case Study
This blog will discuss the installation process for the Express Building Case Study, with details of the finalised project.


